Top Pneumatic Equipment Types You Should Know About?
Pneumatic equipment plays a crucial role in various industries. It utilizes compressed air to operate machinery and tools. Understanding its types can boost efficiency in your operations.
Three main types of pneumatic equipment exist: actuators, compressors, and valves. Actuators convert air pressure into motion. Compressors generate the required air pressure. Valves control the flow of air within systems. Each type serves a distinct function.
Some may overlook the importance of maintenance. Ignoring issues can lead to inefficiencies. Regular checks on pneumatic equipment ensure optimal performance. Understanding these types can enhance productivity and safety in the workplace.
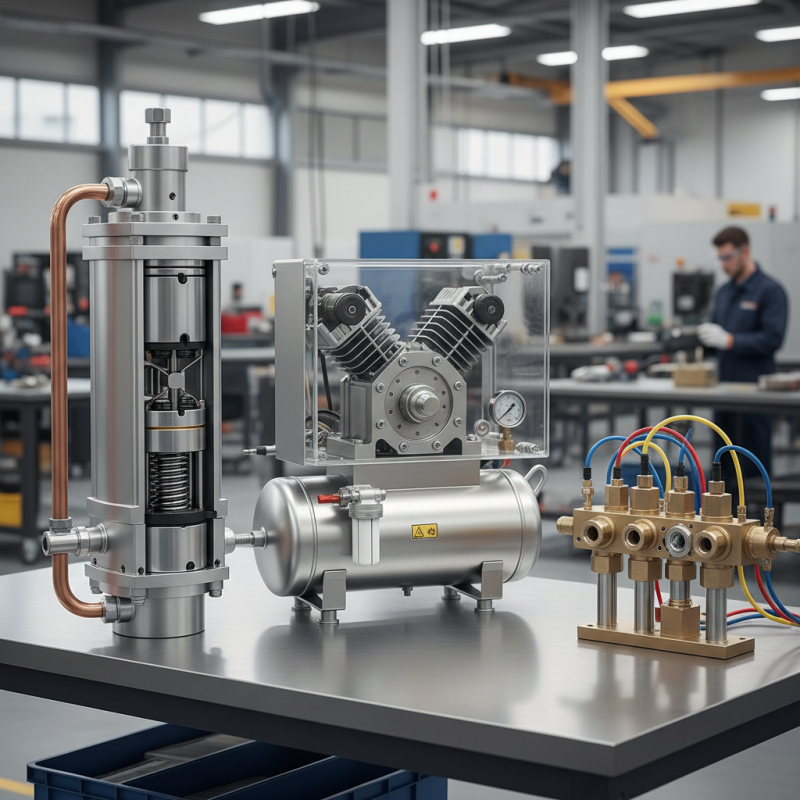

Introduction to Pneumatic Equipment: Overview and Importance
Pneumatic equipment plays a crucial role in various industries today. It utilizes compressed air to perform tasks efficiently. From powering tools to automating processes, these systems are essential for productivity. However, many users don't fully understand their importance.
Pneumatic tools can vary widely in design and application. Examples include air compressors, pneumatic cylinders, and valves. Each type serves a specific function. A well-functioning pneumatic system can significantly enhance efficiency. Yet, improper usage can lead to malfunctions. It’s vital to understand each component's role in the overall system.
Maintenance of pneumatic tools is often overlooked. Regular checks are crucial. Neglecting small issues can result in larger problems down the line. Users should be aware of common pitfalls. Understanding these aspects can lead to better usage and longer life for equipment. Investing time in knowledge is key to maximizing the advantages of pneumatic technology.
Common Types of Pneumatic Tools and Their Applications
Pneumatic tools play a crucial role in various industries. They offer efficiency and precision in tasks ranging from assembly to maintenance. Common pneumatic tools include air compressors, impact wrenches, and spray guns. According to industry reports, the pneumatic tools market is expected to grow by over 6% annually, reflecting their increasing importance.
Air compressors are the backbone of pneumatic systems. They convert power into compressed air, which drives other tools. Impact wrenches are essential for heavy-duty applications. For example, they are used in tire changing and automotive assembly. The power output can reach up to 1,000 foot-pounds, making them incredibly effective. Despite their advantages, operators must ensure proper maintenance to prevent failures.
Spray guns utilize compressed air to atomize paint and coatings. They enable a smooth finish on various surfaces. However, achieving an even coat requires skill. An inconsistent application can lead to wasted materials and time. According to recent surveys, approximately 30% of users experience issues with spray guns due to improper technique or equipment choice. These challenges highlight the need for better training in pneumatic tool usage.
Key Components of Pneumatic Systems and Their Functions
Pneumatic systems play a vital role in various industries. They primarily use compressed air to generate motion, utilizing several key components. One of these components is the air compressor. It serves as the heart of the system, compressing air to produce the necessary pressure. Without a reliable compressor, the entire system can fail.
Another important element is the actuator, often found in two types: pneumatic cylinders and rotary actuators. Pneumatic cylinders create linear motion by converting compressed air into mechanical energy. These cylinders are utilized in applications like assembly lines. Rotary actuators, on the other hand, produce rotational motion. They are crucial for tasks requiring precise positioning.
Additionally, control valves manage airflow and pressure within the system. These valves regulate the direction and speed of movement. It's essential to recognize that even minor leaks in these components can lead to decreased efficiency. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help identify potential issues. Only then can we fully harness the power of pneumatic systems.
Top Pneumatic Equipment Types You Should Know About
| Equipment Type | Key Component | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Air Compressor | Compressor | Converts power into potential energy stored in pressurized air |
| Pneumatic Actuator | Cylinder | Converts compressed air into mechanical motion |
| Pneumatic Valve | Control Valve | Regulates the flow and pressure of air within the system |
| Filter-Regulator | Filter and Regulator | Cleans air and regulates its pressure before it reaches the actuator |
| Pneumatic Tubing | Hoses | Transfers compressed air from one component to another |
| Pressure Switch | Switch | Monitors the system pressure and sends signals when thresholds are exceeded |
Safety Considerations When Using Pneumatic Equipment
When using pneumatic equipment, safety should always be a top priority. According to the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), air pressure can reach dangerous levels, leading to potential accidents. Proper training is essential. Workers must understand how to operate equipment correctly. Without sufficient knowledge, risks increase significantly.
Tip: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Safety goggles and gloves can prevent injuries from debris or unexpected equipment malfunctions. Additionally, ensure that connections are secure and that hoses are not damaged. Regular inspections can reduce the likelihood of mishaps.
Operators should also be aware of noise levels. Prolonged exposure to high noise can lead to hearing loss, which affects many workers in the industry. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends using noise-cancelling headsets for those frequently working with pneumatic tools.
Tip: Create a safety checklist. Include items like checking air pressure limits and inspecting tools before use. Encouraging this practice ensures all personnel remain vigilant about safety measures. Prioritizing these details can cultivate a safer work environment.
Future Trends in Pneumatic Technology and Innovations
The landscape of pneumatic technology is rapidly evolving. New materials and designs make equipment lighter and more efficient. Innovations are not just focused on performance; they also prioritize energy efficiency. Many companies are exploring advanced materials that can withstand higher pressures while reducing weight. Therefore, pneumatic systems become more versatile in various applications.
Automation is a significant trend in this sector. Smart technology allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments. This shift enhances productivity but also presents challenges. Engineers must ensure that systems are both user-friendly and reliable. Unexpected issues can arise, requiring constant adjustments and recalibrations.
Sustainability is also gaining traction. More businesses aim to reduce their carbon footprint. New pneumatic equipment strives to use less energy and produce minimal waste. However, it remains a work in progress. Some components still lag behind in eco-friendliness. Continuous innovation is crucial to overcome these barriers.
Top Pneumatic Equipment Types You Should Know About
This chart illustrates the global market share of various types of pneumatic equipment. As you can see, cylinders lead the market, followed by valves, which play a crucial role in controlling airflow. Compressors and actuators also hold significant shares, while filters, although essential, have a smaller market presence.
Related Posts
-

What is Pneumatic Equipment? Understanding Types and Applications Explained
-

Maximizing Efficiency: Why Integral Drill Rods Are Essential for Modern Drilling Techniques
-

Top 10 Hand Held Rock Drills of 2025: Your Ultimate Buying Guide
-

Best Integral Drill Rod Features and Benefits Explained?
-

How to Choose the Best 30m Depth Rock Drill for Your Project Needs
-

Why Hydraulic Drill Rigs Are Essential for Modern Construction Projects?



